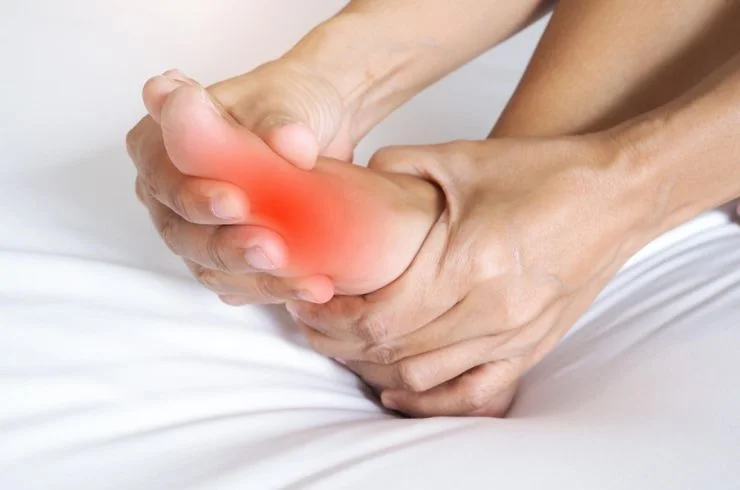
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that occurs when there is damage to the peripheral nerves, which are the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. These nerves carry signals between the body and the brain, controlling sensation, movement, and other functions. When peripheral neuropathy develops, it can cause a range of symptoms, including numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain in the affected areas of the body. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for peripheral neuropathy is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Peripheral neuropathy can be caused by various factors, including diabetes, autoimmune diseases, infections, exposure to toxins or chemicals, trauma or injury to the nerves, vitamin deficiencies, and certain medications. The specific cause of peripheral neuropathy may determine the type of symptoms experienced and the course of the condition.
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can vary depending on the type and severity of nerve damage, as well as the nerves affected. Common symptoms may include numbness or reduced sensation, tingling or burning sensations, sharp or shooting pain, muscle weakness or loss of coordination, sensitivity to touch or temperature changes, and changes in reflexes or muscle tone.
Diagnosing peripheral neuropathy typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and neurological assessment to evaluate symptoms and identify potential underlying causes. Tests such as nerve conduction studies, electromyography (EMG), blood tests, imaging studies such as MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or CT (computed tomography) scans, and skin biopsy may be performed to assess nerve function and rule out other conditions.
Treatment options for peripheral neuropathy focus on managing symptoms, slowing the progression of nerve damage, and addressing underlying causes when possible. Medications such as pain relievers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, or topical treatments may be prescribed to alleviate pain, numbness, or other symptoms. Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy diet, managing blood sugar levels (for individuals with diabetes), quitting smoking, avoiding alcohol, and regular exercise may help improve nerve function and overall well-being.
In addition to medication and lifestyle changes, other treatment approaches such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, acupuncture, or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) may be recommended to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals with peripheral neuropathy.
Although peripheral neuropathy can be challenging to manage, early diagnosis and intervention, along with a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs, can help reduce symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall function and quality of life. Close collaboration between healthcare providers, including neurologists, primary care physicians, physical therapists, and other specialists, is essential for effectively managing peripheral neuropathy and optimizing outcomes for affected individuals.